News | TCTAP 2023
Physiologic Approach for Non-LM Bifurcation Lesions
All Bifurcation PCI

Bon-Kwon Koo
Seoul National University Hospital, Korea
A recent lecture at TCTAP 2023, ‘All Bifurcation PCI’ highlighted the clinical relevance of side branches and emphasized the importance of weighing risk and benefit when guiding the bifurcation percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) strategy.
Bon-kwon Koo, MD (Seoul National University Hospital, Korea) introduced a novel algorithm for a physiological approach, developed collaboratively by the Korean, Japanese, and European Bifurcation Clubs. This algorithm aims to provide a comprehensive framework for managing coronary bifurcation lesions. According to the algorithm, if the side branch is deemed not clinically relevant, the primary objective is just to maintain thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 3 flow in the side branch. This determination is primarily based on angiographic assessment.
He also introduced the SNuH score, which was developed a decade ago and incorporated into the Bifurcation Academic Research Consortium (Bif-ARC) in 2022 to assess the clinical significance of side branches. The score takes into account vessel size (diameter >2.5 mm), the number of diagonal branches (≤2), and the absence of branches below the target branch. Furthermore, a simple decision tree approach was also introduced which is based on the analysis of over a thousand cases (Figure 1). It revealed that only 15% of side branches supply more than 10% of the entire myocardium. However, the likelihood of a diagonal branch supplying more than 10% of the entire myocardium varies according to the coronary anatomy. If a single diagonal branch is present without left circumflex dominance, the likelihood of supplying more than 10% of the myocardium rises to 74%.
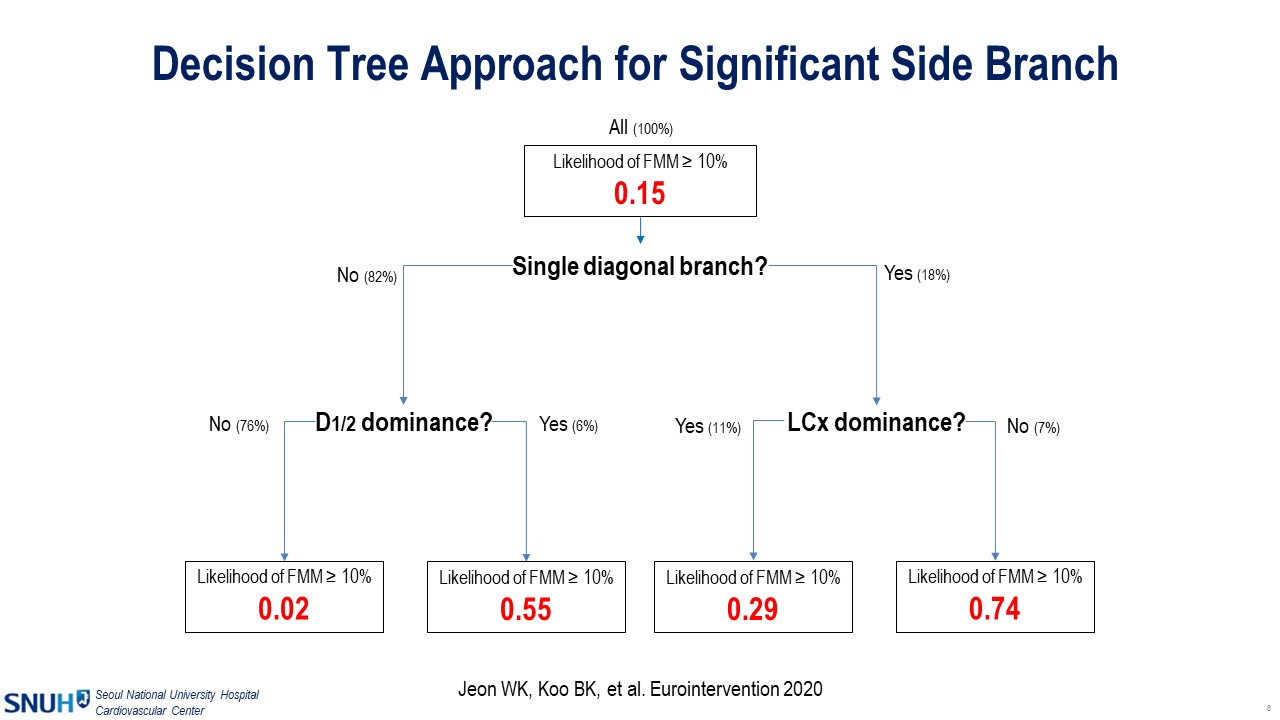
Figure 1. Decision tree approach for significant side branch
In cases where the side branch is clinically relevant, the proposed algorithm by Korean, Japanese, and European Bifurcation Clubs recommends provisional side branch stenting. Following stenting, functional assessments such as fractional flow reserve (FFR) or non-hyperemic methods are required. Additional side branch intervention is indicated if these values fall below the thresholds. In a previous retrospective analysis, FFR data of jailed left circumflex artery (LCX) after left main-left anterior descending artery (LM-LAD) crossover stenting revealed that a low FFR value (<0.80) was associated with a three-fold increase in target lesion failure over a 5-year follow-up period (Figure 2). And this additional side branch procedure should not be determined by angiographic image only, because numerous studies have demonstrated discordance between angiographic and functional assessments of jailed side branches. He also mentioned that side branch wiring with a pressure wire can be tricky, and the procedural failure rate stands at approximately 3.9% based on data from six studies. Considering the clinical benefits and risks associated with side branch pressure wire advancement, it is advisable to focus on short and ostial lesions in large side branches for functional assessment after crossover stenting.
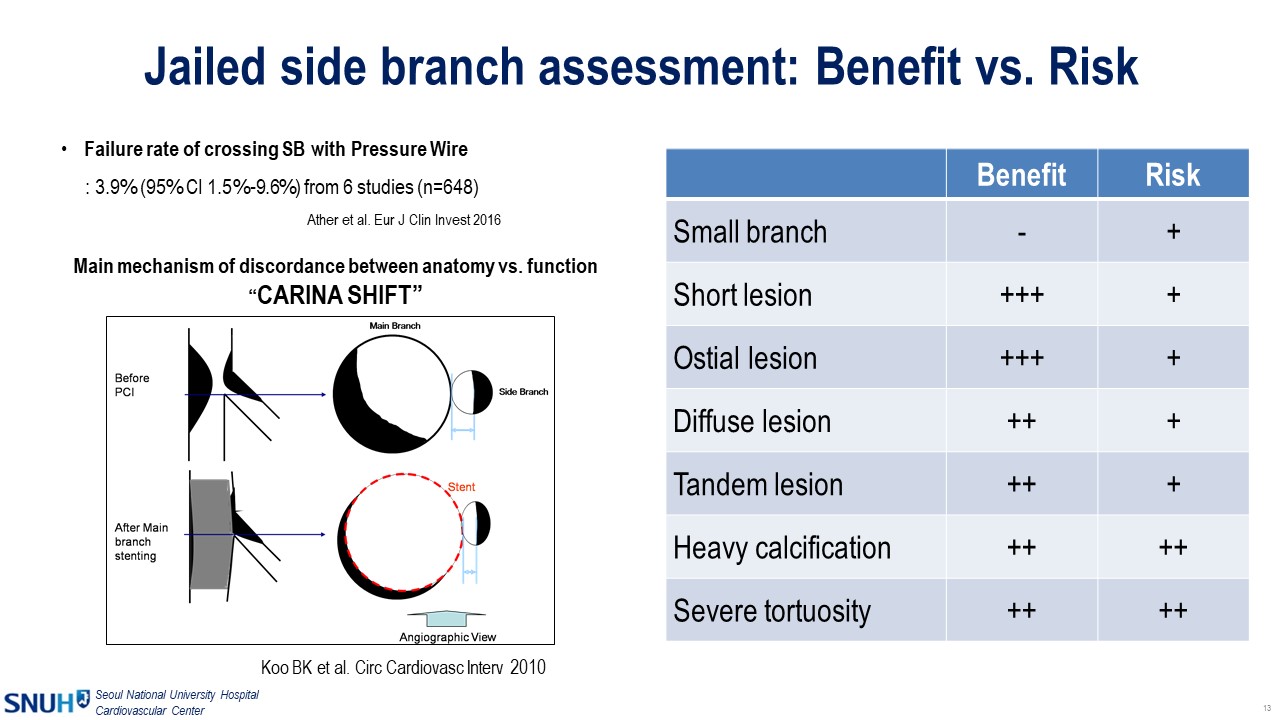
Figure 2. Benefit and risk assessment of jailed side branch
When side branch disease necessitates a two-stent technique, the proposed algorithm emphasizes the optimization guided by intravascular imaging. While functionally complete revascularization is an important goal, it is crucial to consider other parameters such as sufficient stent area, minimal stent overlap, and avoidance of malposition, as these factors can influence adverse events.
Discrepancies between FFR values and angiographic images after LM to LAD crossover stenting are not uncommon. In such cases, functional assessment can help avoid unnecessary procedures for patients. Dr. Koo highlighted the importance of having adequate knowledge to assess potential mismatches and reverse mismatches in FFR values in jailed LCX. Operators should remain mindful of potential factors that can lead to inaccurate measurements of FFR in jailed LCX, including the presence of other remnant significant stenoses, guiding catheter damping, inadequate hyperemia, or coronary spasm.
The field of bifurcation procedures is evolving, with several new concepts emerging. Examples include physiological index-guided drug-coated balloon (DCB) treatments and the co-registration of imaging and physiology to enhance the understanding of the true target for revascularization. Image-based physiological assessments, such as CT-derived FFR, are also being utilized to guide revascularization strategies.
Meet the Experts over Breakfast
All Bifurcation PCI
Monday, May 8, 7:00 AM - 7:50 AM
Presentation Theater 1, Vista 3, B2
Edited by

Yong-Hoon Yoon, MD
Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Korea (Republic of)

Bon-Kwon Koo
Seoul National University Hospital, Korea
A recent lecture at TCTAP 2023, ‘All Bifurcation PCI’ highlighted the clinical relevance of side branches and emphasized the importance of weighing risk and benefit when guiding the bifurcation percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) strategy.
Bon-kwon Koo, MD (Seoul National University Hospital, Korea) introduced a novel algorithm for a physiological approach, developed collaboratively by the Korean, Japanese, and European Bifurcation Clubs. This algorithm aims to provide a comprehensive framework for managing coronary bifurcation lesions. According to the algorithm, if the side branch is deemed not clinically relevant, the primary objective is just to maintain thrombolysis in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 3 flow in the side branch. This determination is primarily based on angiographic assessment.
He also introduced the SNuH score, which was developed a decade ago and incorporated into the Bifurcation Academic Research Consortium (Bif-ARC) in 2022 to assess the clinical significance of side branches. The score takes into account vessel size (diameter >2.5 mm), the number of diagonal branches (≤2), and the absence of branches below the target branch. Furthermore, a simple decision tree approach was also introduced which is based on the analysis of over a thousand cases (Figure 1). It revealed that only 15% of side branches supply more than 10% of the entire myocardium. However, the likelihood of a diagonal branch supplying more than 10% of the entire myocardium varies according to the coronary anatomy. If a single diagonal branch is present without left circumflex dominance, the likelihood of supplying more than 10% of the myocardium rises to 74%.

In cases where the side branch is clinically relevant, the proposed algorithm by Korean, Japanese, and European Bifurcation Clubs recommends provisional side branch stenting. Following stenting, functional assessments such as fractional flow reserve (FFR) or non-hyperemic methods are required. Additional side branch intervention is indicated if these values fall below the thresholds. In a previous retrospective analysis, FFR data of jailed left circumflex artery (LCX) after left main-left anterior descending artery (LM-LAD) crossover stenting revealed that a low FFR value (<0.80) was associated with a three-fold increase in target lesion failure over a 5-year follow-up period (Figure 2). And this additional side branch procedure should not be determined by angiographic image only, because numerous studies have demonstrated discordance between angiographic and functional assessments of jailed side branches. He also mentioned that side branch wiring with a pressure wire can be tricky, and the procedural failure rate stands at approximately 3.9% based on data from six studies. Considering the clinical benefits and risks associated with side branch pressure wire advancement, it is advisable to focus on short and ostial lesions in large side branches for functional assessment after crossover stenting.

When side branch disease necessitates a two-stent technique, the proposed algorithm emphasizes the optimization guided by intravascular imaging. While functionally complete revascularization is an important goal, it is crucial to consider other parameters such as sufficient stent area, minimal stent overlap, and avoidance of malposition, as these factors can influence adverse events.
Discrepancies between FFR values and angiographic images after LM to LAD crossover stenting are not uncommon. In such cases, functional assessment can help avoid unnecessary procedures for patients. Dr. Koo highlighted the importance of having adequate knowledge to assess potential mismatches and reverse mismatches in FFR values in jailed LCX. Operators should remain mindful of potential factors that can lead to inaccurate measurements of FFR in jailed LCX, including the presence of other remnant significant stenoses, guiding catheter damping, inadequate hyperemia, or coronary spasm.
The field of bifurcation procedures is evolving, with several new concepts emerging. Examples include physiological index-guided drug-coated balloon (DCB) treatments and the co-registration of imaging and physiology to enhance the understanding of the true target for revascularization. Image-based physiological assessments, such as CT-derived FFR, are also being utilized to guide revascularization strategies.
Meet the Experts over Breakfast
All Bifurcation PCI
Monday, May 8, 7:00 AM - 7:50 AM
Presentation Theater 1, Vista 3, B2
Edited by

Yong-Hoon Yoon, MD
Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Korea (Republic of)


Leave a comment