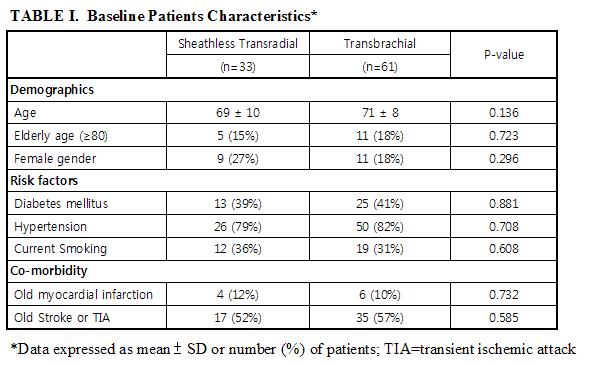
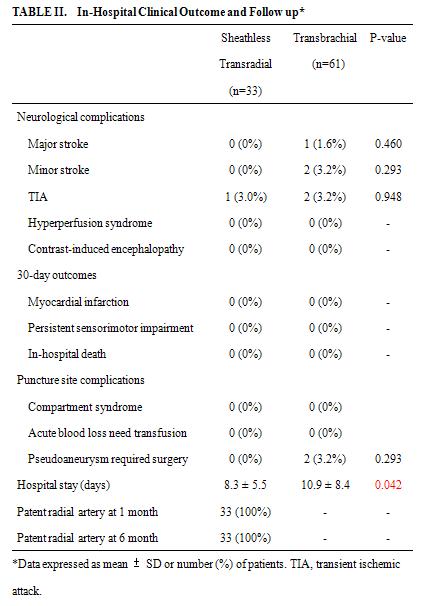
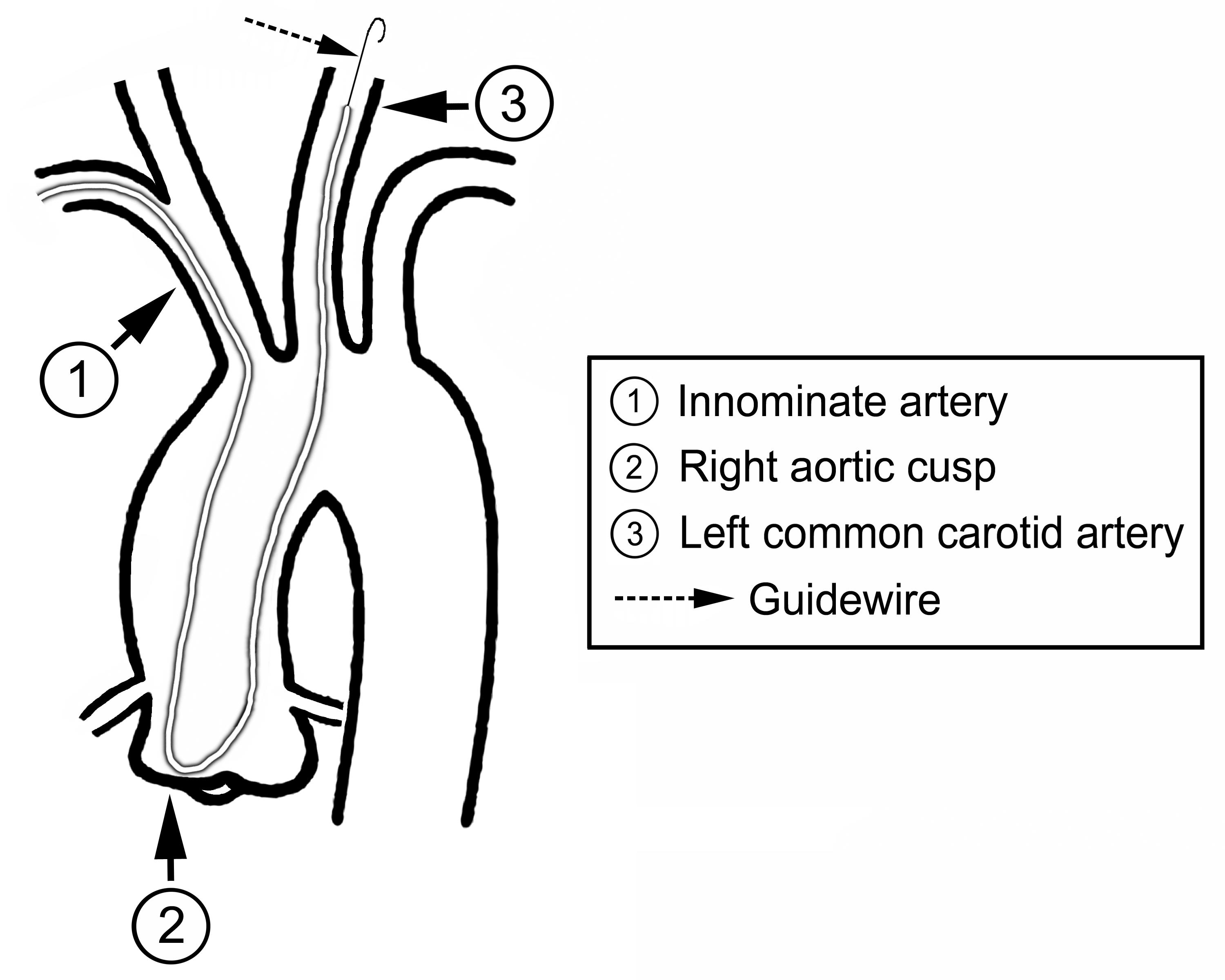
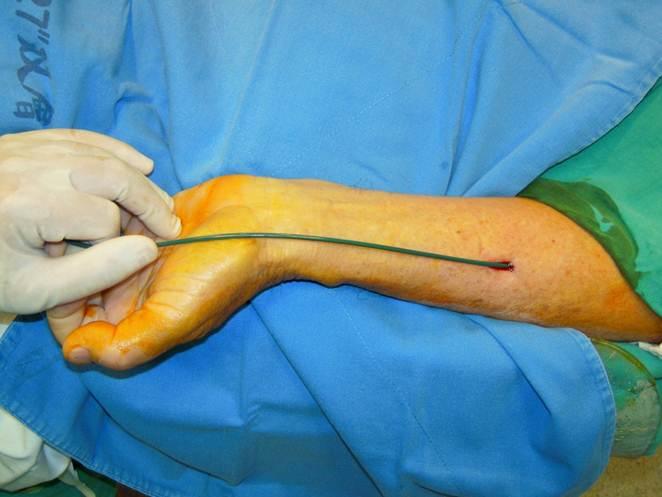
This sheathless TRA CAS technique offered 100% diagnostic and procedure success. There were no baseline characteristics differences between TRA and TBA (Table 1). Only one patient (3.1%) experienced transient ischemia attack (TIA) during the procedure and immediately recovery during hospitalization. There were no major complications 0% (major stroke or 30 day in-hospital death), nor radial access site complications (compartment syndrome, or acute blood loss need blood transfusion), as compared with TBA CAS, stroke occurred in 3/61 (one major & 2 minor strokes, 4.9%), and 2 brachial pseudo-aneurysm demanding surgical repair (Table 2). Significant longer hospital stay in TBA than sheathless TRA in this study (10.9 ± 8.4 v.s. 8.3 ± 5.5, p=0.042). All radial arteries were patent during 1 month and 6 month clinical follow up.